Have you ever gone to the grocery store and noticed that the prices of your favourite products have gone up? It’s not just your imagination – grocery items do go up in price, and it’s a phenomenon that affects consumers all over the world. But why does this happen?
Recent statistics released by the ABS have shown that over the year 2022, prices on food and non-alcoholic beverages have increased by 9.2%.
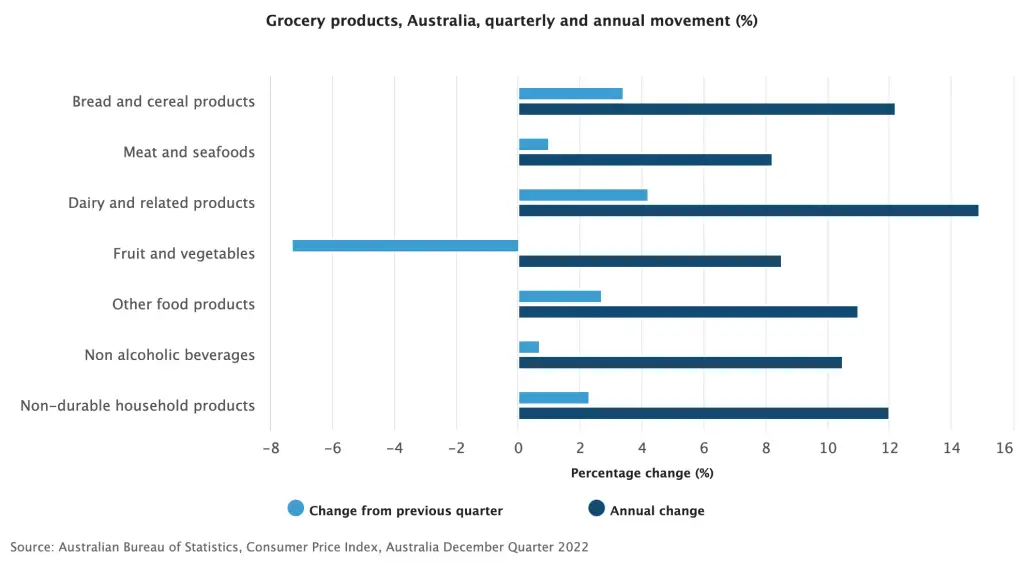
There are a number of factors that can cause grocery prices to rise. One of the most significant is inflation, which is the general increase in prices over time. Inflation can be caused by a variety of factors, including changes in the economy, fluctuations in the value of the currency, and changes in the supply and demand for goods and services. When inflation occurs, the cost of producing and transporting goods increases, and these costs are often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Another factor that can cause grocery prices to rise is changes in the supply and demand for specific products. For example, if there is a drought that affects the production of wheat, the price of bread may go up. Similarly, if there is a sudden increase in demand for a particular product, such as avocados, the price may rise as well. These fluctuations in supply and demand can be caused by a variety of factors, including changes in consumer preferences, weather patterns, and global events.
Factors that Affect Grocery Prices
Supply and Demand
One of the primary factors that affect grocery prices is the law of supply and demand. When the demand for a particular product increases, but the supply remains the same or decreases, the price of that product will increase. Similarly, when the demand for a product decreases, but the supply remains the same or increases, the price of that product will decrease. This is why prices of seasonal fruits and vegetables tend to fluctuate throughout the year.
Weather and Natural Disasters
Weather patterns and natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and hurricanes can have a significant impact on the prices of grocery items. For example, if there is a drought in a region that produces a significant amount of a particular crop, the supply of that crop will decrease, causing prices to rise. Similarly, if a hurricane destroys a significant amount of farmland, the supply of crops will decrease, leading to an increase in prices.
Transportation Costs
The cost of transporting grocery items from the farm to the store can also impact the price of these items. When the cost of fuel increases, the cost of transporting goods also increases, which can lead to higher prices for consumers. Additionally, if there are disruptions in the transportation system, such as a strike or a natural disaster, the cost of transporting goods can increase, leading to higher prices for consumers.
Cost of Production
The cost of producing grocery items can also impact their price. Factors such as labour costs, cost of raw materials, and cost of equipment can all impact the cost of production. When these costs increase, producers may need to increase their prices in order to maintain profitability.
Government Policies and Regulations
Taxes and Tariffs
One of the primary ways that government policies and regulations affect grocery prices is through taxes and tariffs. When the government imposes taxes on certain goods and services, the cost of producing and distributing those goods goes up, which can result in higher prices for consumers. Similarly, when tariffs are imposed on imported goods, the cost of those goods goes up, which can also lead to higher prices for consumers.
Minimum Wage Laws
Another way that government policies and regulations can impact grocery prices is through minimum wage laws. When governments increase the minimum wage, businesses may be forced to raise prices in order to cover the increased labor costs. This can lead to higher prices for consumers, which can be particularly challenging for those on fixed incomes or with limited budgets.
Subsidies and Trade Agreements
Finally, subsidies and trade agreements can also play a role in grocery prices. When governments provide subsidies to certain industries, those industries may be able to produce goods at a lower cost, which can result in lower prices for consumers. Similarly, trade agreements can impact the price of imported goods, either by lowering tariffs or by allowing for greater competition, which can result in lower prices for consumers.
Overall, government policies and regulations can have a significant impact on the price of groceries. By understanding how taxes, tariffs, minimum wage laws, subsidies, and trade agreements can impact prices, consumers can make more informed decisions about their purchases and better plan for the impact of these policies on their budgets.
Global Economic Trends
The global economy is a complex system that can impact grocery prices in various ways. Here are some key economic trends that can affect the prices of grocery items:
Inflation and Deflation
Inflation and deflation are two economic concepts that can impact the prices of grocery items. Inflation occurs when the general price level of goods and services in an economy increases over time. This can happen due to factors like an increase in demand, a decrease in supply, or an increase in the cost of production. Deflation, on the other hand, occurs when the general price level of goods and services in an economy decreases over time. This can happen due to factors like a decrease in demand, an increase in supply, or a decrease in the cost of production.
Exchange Rates
The exchange rate is the value of one currency in relation to another currency. Exchange rates can impact the prices of grocery items, especially if a country relies heavily on imports. If the exchange rate of a country’s currency decreases, the cost of importing goods increases, which can lead to higher grocery prices.
Economic Growth and Recession
Economic growth and recession can also impact the prices of grocery items. During times of economic growth, people tend to have more disposable income, which can lead to an increase in demand for certain goods, including grocery items. This can lead to higher prices. On the other hand, during times of recession, people tend to have less disposable income, which can lead to a decrease in demand for certain goods, including grocery items. This can lead to lower prices.
Consumer Behaviour
Brand Loyalty
Consumers tend to stick with their preferred brands when shopping for groceries. This is because they trust the quality and consistency of those brands. When the prices of these brands go up, consumers may still choose to purchase them, even if it means spending more money. This loyalty to certain brands can make it difficult for new brands to enter the market and compete.
Consumer Preferences
Consumers have different preferences when it comes to grocery shopping. Some may prefer organic or locally-sourced products, while others may prioritize convenience and price. When prices go up, consumers may switch to cheaper alternatives or change their shopping habits altogether. Retailers often take advantage of these preferences by offering promotions and discounts on certain products.
Retailer Strategies
Retailers play a significant role in determining the prices of grocery items. They may use various strategies to increase their profits, such as raising prices during peak demand periods or charging more for popular brands. Retailers may also offer discounts on certain products to attract customers and increase sales. These strategies can have a significant impact on the prices of grocery items.
Conclusion
In conclusion, consumer behaviour plays a significant role in the prices of grocery items. Brand loyalty, consumer preferences, and retailer strategies all contribute to price fluctuations. While it can be frustrating for consumers to see prices go up, it is important to understand the various factors at play and make informed decisions when shopping for groceries.

